Osmosis Can Only Occur if Water Travels Through the
A Consummate Resources GUIDE ON OSMOSIS
Do you know that depending upon the size of your trunk, 55% to 78% is water? Osmosis is 1 of the virtually important biological processes in living things for it is the method allowing h2o to spread effectually the cells; without water, the cells volition die. This Resource Guide on Osmosis will illustrate how important this process is to survival.
Overview of Osmosis
Osmosis is the passage of water from a low solute concentration expanse through a semi-permeable membrane to a high solute concentration expanse to equalize the solute concentrations on both sides. A solvent is the base of operations substance, where a solute is being dissolved and the result is the solution. Through osmosis, water is provided to the cells of your body; information technology plays a meaning function in the preservation of life. It is this procedure that helps plants receive water and is even used in kidney dialysis.
- Blitheness: How Osmosis Work – Teachers discussing the topic of osmosis can use this link to give an interesting presentation of osmosis.
- Diffusion and Osmosis - Learn about the difference between diffusion and osmosis on this website.
Factors Affecting the Charge per unit of Osmosis
Temperature - The higher the temperature, the faster the water molecules move across the semi permeable membrane.
Surface Expanse - The larger the surface expanse, the more space for the molecules to motility hands across; the smaller the area, the more restricted the movements of the molecules and the slower the movement.
Difference in Water Potential – The higher the departure in water potential, the faster the osmosis; for the lesser water molecules are in the region of low concentration, more water molecules from the region of college concentration can enter faster and easier.
Pressure – The more the pressure, the faster the molecules will move for they are being pushed faster across a depression concentration.
Concentration gradient - The movement of osmosis is affected by the concentration gradient; the lower the concentration of the solute within a solvent, the faster osmosis volition occur in that solvent.
Light and nighttime – They are also factors of osmosis; since the brighter the low-cal, the faster osmosis takes identify.
- Sources near Osmosis – These are various papers discussing factors affecting osmosis.
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is a colligative belongings. In other words, it depends on the tooth concentration of the solute just not on its density. It is the pressure which is applied to a solution to preclude the in catamenia of water across a semi permeable membrane, or simply put information technology is the pressure level required to stop osmosis. Osmotic pressure is shown when water molecules that attempt to cantankerous the semi permeable membrane are prevented from doing so.
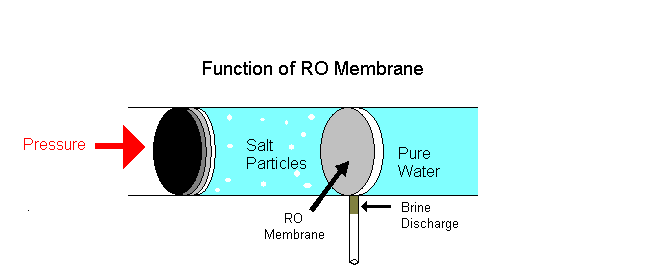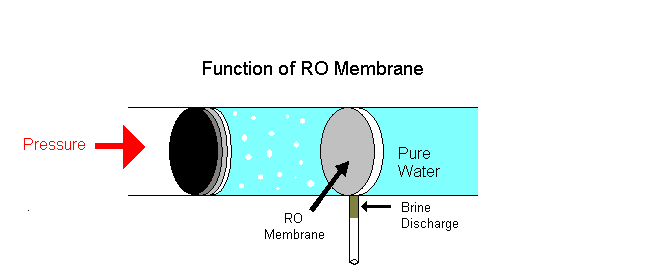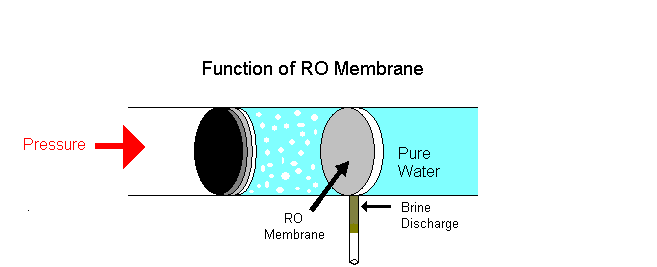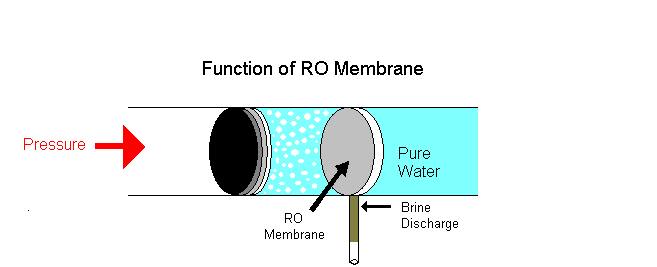
Example of osmotic pressure: Place some raisins in a cup of water for a few hours, notice that they volition swell and if kept longer will burst. The reason is that as water continues to diffuse into the membranous cover of the raisins; this influx of h2o builds upward an internal pressure and upon reaching its limit the outer pare of the raisin will outburst once it can no longer conduct the pressure level.
- Osmotic Pressure Calculation – This is a good illustration on how to calculate osmotic pressure.
- Visual of Osmotic Pressure – Do you know what osmotic pressure is? This site will give you a visual caption.
- Lesson Program for Osmotic Pressure – Teachers who are teaching lessons in osmotic pressure, can follow this lesson plan model.
Osmotic Gradient
The osmotic gradient is the deviation between two concentration solutions at either side of a semi permeable membrane that distinguishes the different per centum of a specific particle concentration that is dissolved in a solution. The osmotic gradient acts on solutions having a semi permeable membrane between them; assuasive h2o to diffuse betwixt the ii solutions toward the solution with the higher concentration. Eventually, h2o with college concentration will be equally diffused to the side of a lesser concentration. It creates equilibrium for water continues to flow equally both ways, resulting in a stabilized solution.
- Osmotic Gradient in Kidney Medulla – This paper describes how the osmotic slope in the kidney medulla is built upwards. This topic is among the well-nigh complex mechanisms presented to students of physiology.
- PDF Experiment on Osmosis Slope – Through experimentation, osmosis gradient will be clearly illustrated.
Variations
 i. Reverse osmosis is a separation process using pressure to force a solvent to pass through a semi permeable membrane that keeps the solute on ane side and directs the pure solvent to the other side. In other words, this is the process where osmotic force per unit area is applied to force a solvent from an expanse of high solute concentration towards an area of low solute concentration.
i. Reverse osmosis is a separation process using pressure to force a solvent to pass through a semi permeable membrane that keeps the solute on ane side and directs the pure solvent to the other side. In other words, this is the process where osmotic force per unit area is applied to force a solvent from an expanse of high solute concentration towards an area of low solute concentration.
Examples: Equally a solution of h2o shortage, rain water is purified as drinking water. Big industries employ reverse osmosis to remove minerals from their boiler water to be recycled. Reverse osmosis is the technique used in liver dialysis. A dialysis machine mimics the function of the kidneys.
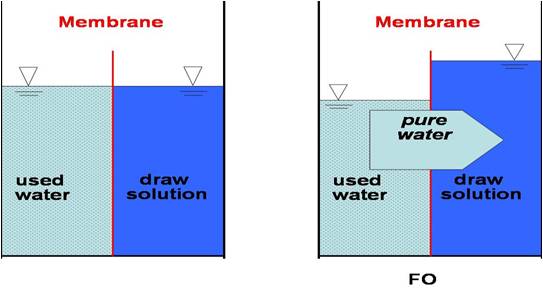
2. Frontward osmosis uses osmosis to directly split water from a feed solution with unwanted solutes. A draw solution uses the feed solution to force water through a semi permeable membrane; resulting in the feed solution becoming concentrated and the depict solution becoming diluted. The describe solution which is at present diluted can exist used with an ingestible solute similar glucose or transmitted to a secondary process from the draw solute.
Examples of forward osmosis are desalination, water purification, and nutrient processing.
- Pros and Cons of Opposite Osmosis – You know about the bright side of contrary osmosis, at present let's look at the night side.
- Health Benefit of Contrary Osmosis – Through the process of opposite analysis, those suffering from liver ailments are able to benefit from liver dialysis.
- Desalination – The cadre process of desalination is the contrary osmosis process.
- Experiments on Frontward Osmosis - This site contains an experiment conducted about forward osmosis.
Types of Solutions
There are iii different types of solutions that are used to describe water motility. The beginning is the hypertonic solution. The hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the other solution types. When an animal prison cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it loses water and shrinks. This is called a flaccid prison cell. The second type of solution is called a hypotonic solution. This solution is one which has a low solute concentration when compared to the other solutions. When an animal cell is placed in this kind of solution, the prison cell absorbs all the water and becomes bloated. The terminal solution type is the isotonic solution type. This solution has no difference in solute concentration across the semi permeable membrane, therefore has no net motility of water across the membrane.
- Iii Types of Solutions – Know the difference between the three types of solutions.
- Hypotonic Solution – Larn more most hypotonic solution and how it differs from the other solutions.
Additional Resources
- Water Purifier Using Osmosis – This is a new major development which removes undesirable chemicals, materials, and other biological components from raw water.
- Osmosis Simulation – The process of osmosis is shown in this simulation along with a description.
- Drinking H2o Treatment: Reverse Osmosis – A comprehensive PDF article that discusses how reverse osmosis helps in treating drinking h2o.
Source: https://www.freedrinkingwater.com/resource-a-complete-resource-guide-to-osmosis.htm
0 Response to "Osmosis Can Only Occur if Water Travels Through the"
Post a Comment